Android XR Light Estimation
The Android XR Light Estimation extension provides real time lighting information from the player's environment.
This can allow virtual objects to be rendered with lighting that more realistically matches the real world environment that they are being placed in.
There are two ways to use Android XR Light Estimation:
The OpenXRAndroidLightEstimation node, which can automatically update
DirectionalLight3DandWorldEnvironmentnodes in your scene. Or,Passing data from the OpenXRAndroidLightEstimationExtensionWrapper singleton to custom shaders.
Note
Check out the Android XR Light Estimation Sample Project for a working demo that shows both approaches.
Project Settings
To use Android XR Light Estimation, the OpenXR extension must be enabled in project settings. The extension setting can be found in Project Settings under the OpenXR section. The Light Estimation setting should be listed under Extensions in the Androidxr subcategory.
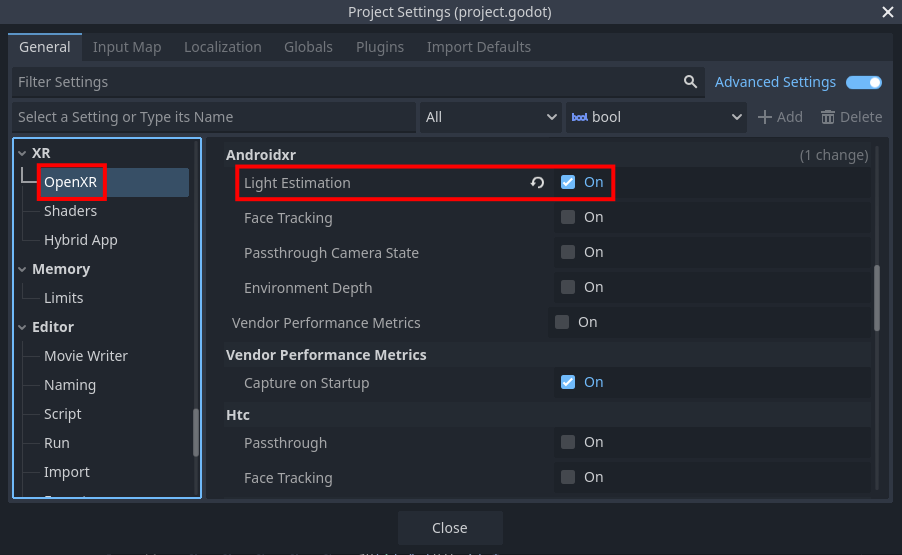
Starting and stopping
Before Android XR Light Estimation can be used, it needs to be started:
if OpenXRAndroidLightEstimationExtensionWrapper.is_light_estimation_supported():
OpenXRAndroidLightEstimationExtensionWrapper.start_light_estimation()
This will only work if there is an active OpenXR session. You can connect
to the OpenXRInterface.session_begun signal to run code right when
the session starts.
There is a performance cost to using Android XR Light Estimation, so you should only start it when needed, and stop it when no longer needed. For example, if your application has both a VR and AR mode, you should make sure that Android XR Light Estimation is only running in AR mode.
Permissions
Light Estimation requires the android.permission.SCENE_UNDERSTANDING_COARSE
permission, which will automatically be requested when your application
starts up if Android XR Light Estimation is enabled, as well as the
Automatically Request Runtime Permissions setting.
If the user hasn't granted this permission previously, they will be
shown a prompt, asking them to allow scene understanding.
However, Light Estimation won't actually work until after they've granted
the permission, so you may want connect to the
SceneTree.on_request_permission_result signal, for example:
func _ready() -> void:
get_tree().on_request_permissions_result.connect(_on_request_permissions_result)
func _on_request_permissions_result(p_permission: String, p_granted: bool) -> void:
if p_permission == "android.permission.SCENE_UNDERSTANDING_COARSE" and p_granted:
# Retry starting light estimation...
pass
Using the OpenXRAndroidLightEstimation node
The easiest way to use Android XR Light Estimation is by adding an
OpenXRAndroidLightEstimation node
to your scene, and updating the Directional Light and/or World Environment
properties to point to your DirectionalLight3D and/or WorldEnvironment nodes,
respectively.
This way you don't need to make any changes to the materials or shaders used in your project - the light estimation data will be incorporated automatically.
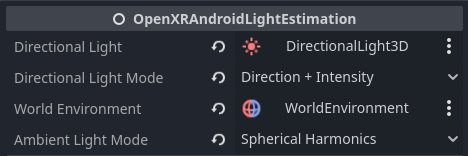
If Directional Light is set, then the Directional Light Mode will
determine how the DirectionalLight3D is updated:
Disabled: The directional light won't be updated at all. This is useful for temporarily disabling light estimation's effect on the light.
Direction Only: Only update the direction of the directional light.
Direction + Intensity: Update the direction and intensity of the directional light.
Direction + Color + Intensity: Update the direction, color, and intensity of the directional light.
If World Environment is set, then the Ambient Light Mode will
determine how the WorldEnvironment is updated:
Disabled: The world environment won't be updated at all. This is useful for temporarily disabling light estimation's effect on the world environment.
Color: Only update the environment's ambient color.
Spherical Harmonics: Use spherical harmonics from the light estimation data to update the environment's radiance map.
Using a custom shader
If the way that the OpenXRAndroidLightEstimation node incorporates the light estimation
data isn't to your liking, you can get the data yourself and pass it to custom shaders.
There are a few different types of data that can be provided, so first you'll need to update the OpenXRAndroidLightEstimationExtensionWrapper.light_estimate_types property with the types that you need.
For example:
OpenXRAndroidLightEstimationExtensionWrapper.light_estimate_types = \
OpenXRAndroidLightEstimationExtensionWrapper.LIGHT_ESTIMATE_TYPE_DIRECTIONAL_LIGHT | \
OpenXRAndroidLightEstimationExtensionWrapper.LIGHT_ESTIMATE_TYPE_SPHERICAL_HARMONICS_TOTAL
Then, every frame, you can update the data, see if it's changed since the previous frame, and then update your shader's parameters:
var last_material_update := 0
func _process(_delta: float) -> void:
var ale = OpenXRAndroidLightEstimationExtensionWrapper
if ale.is_light_estimation_started():
var next_update = ale.get_last_updated_time()
if next_update > last_material_update and ale.is_spherical_harmonics_total_valid():
last_material_update = next_update
var coefficients = ale.get_spherical_harmonics_total_coefficients()
# Note: You may want to process the coefficients - see the sample project for an example.
# Update shader parameters on my custom material.
CUSTOM_AMBIENT_MATERIAL.set_shader_parameter("coefficients", coefficients)
CUSTOM_AMBIENT_MATERIAL.set_shader_parameter("rotation", XRServer.world_origin.basis)
Each of the types of data has its own "valid method" that should be called before accessing that data. For example, in the code snippet above, we called is_spherical_harmonics_total_valid() before calling get_spherical_harmonics_total_coefficients().
Take a look at the sample project for a complete example of using a custom shader for ambient lighting.